| 关联规则 | 关联知识 | 关联工具 | 关联文档 | 关联抓包 |
| 参考1(官网) | |
| 参考2 | |
| 参考3 |
研究人员发现一个新的勒索软件Zenis,在执行时如果发现注册表键值HKEY_CURRENT_USER \ SOFTWARE \ ZenisService“Active”或者文件名不是iis_agent32.exe,则不会对计算机进行加密,如果检查通过则会使用AES加密文件,删除备份。目前还不知道该勒索软件的传播方式。 [出自:jiwo.org]
A
new ransomware was discovered this week by MalwareHunterTeam called Zenis Ransomware. While it is currently unknown how Zenis is being distributed, multiple victims have already become infected with this ransomware. What is most disturbing about Zenis is that it not encrypts your files, but also purposely deletes your backups.
When MalwareHunterTeam found the first sample, it was utilizing a custom encryption method when encrypting files. The latest version, and the one we will discuss in this article, utilizes AES encryption to encrypt the files.
At this time there is no way to decrypt Zenis encrypted files, but Michael Gillespie is analyzing the ransomware for weaknesses. Therefore, if you are infected with Zenis, do not pay the ransom. Instead you can receive help or discuss this ransomware in our dedicated Zenis Ransomware help & support topic.
Below is a brief decryption of how the Zenis ransomware encrypts a computer compiled from analysis by MalwareHunterTeam, Michael, and myself.
As previously stated, we do not know how the Zenis Ransomware is currently being distributed. Based on the elusiveness of the ransomware samples and comments from infected people, it could be distributed via hacked Remote Desktop services.
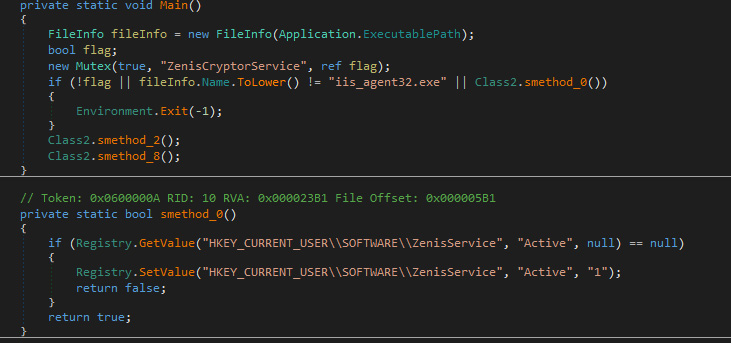
When executed, the current Zenis Ransomware variant will perform two checks to see if it should begin encrypting the comptuer. The first check is to see if the file that executed is named iis_agent32.exe, with this check being case insensitive. The other check is to see if a registry value exists called HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\ZenisService "Active".
If the registry value exists or the file is not named iis_agent32.exe, it will terminate the process and not encrypt the computer.
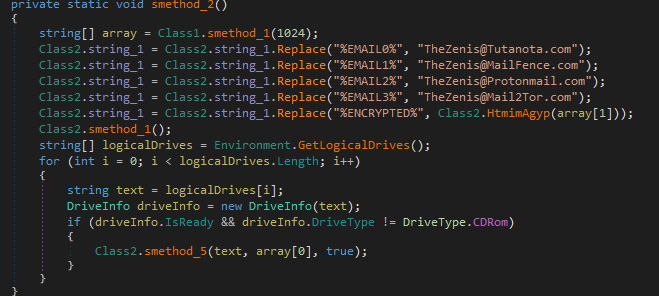
If it passes the checks, it will then begin to get the ransom note ready by filling in some information, such as emails and encrypted data.
After that is completed it will execute the following commands to delete the shadow volume copies, disable startup repair, and clear event logs.
Zenis will then search for various processes and terminate them. The processes terminated are:
Now that it has prepared the system to its liking, it will begin encrypting the files on the computer. It does this by scanning the drives on the computer for files with certain extensions. If it finds a file that matches one of the following extensions, it will encrypt it using a different AES key for each file.
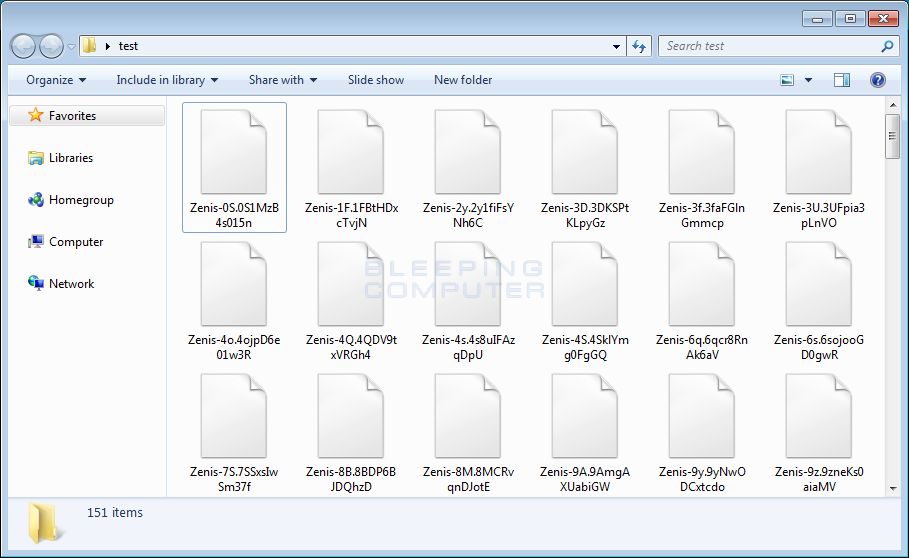
When encrypting a file it will change the file name to the following format. Zenis-[2 random chars].[12 random chars]. For example, test.jpg would be encrypted and renamed to something like Zenis-4Q.4QDV9txVRGh4. The original file name and the AES key use to encrypt the file will be encrypted and saved to end of the file.
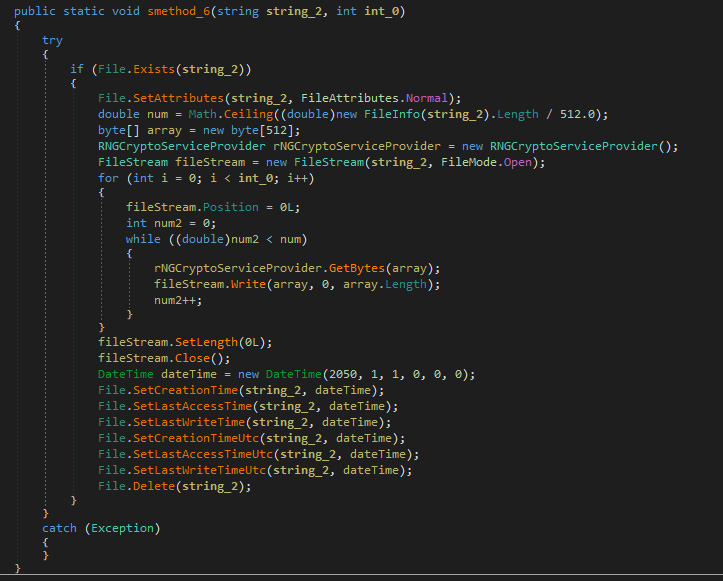
When looking for files to encrypt, if it finds files associated with backup files, it will overwrite them three times and then delete them. This is to make it more difficult for the victim to restore files from a backup.
The list of extensions targeted for deletion are:
While encrypting, it will also create ransom notes named Zenis-Instructions.html in every file that it traverses. This ransom note contains instructions on how to contact the ransomware developer in order to get their files back. The current email addresses included in the ransom notes are TheZenis@Tutanota.com, TheZenis@MailFence.com, TheZenis@Protonmail.com, and TheZenis@Mail2Tor.com.
The reason they ask for the ransom note is because it contains a hidden base64 encoded string that can be decrypted using the private RSA key that only the ransomware developer has possession of. When this data is decrypted, the ransomware developer can decrypt the sample file sent to them or create a decryptor.
As previously said, this ransomware is currently being analyzed for weaknesses, so please do not pay the ransomware.
In order to protect yourself from ransomware in general, it is important that you use good computing habits and security software. First and foremost, you should always have a reliable and tested backup of your data that can be restored in the case of an emergency, such as a ransomware attack.
As Zenis Ransomware may be installed via hacked Remote Desktop services, it is very important to make sure its locked down correctly. This includes making sure that no computers running remote desktop services are connected directly to the Internet. Instead place computers running remote desktop behind VPNs so that they are only accessible to those who have VPN accounts on your network.
It is also important to setup proper account lockout policies so that it makes it difficult for accounts to be brute forced over Remote Desktop Services.
You should also have security software that incorporates behavioral detections to combat ransomware and not just signature detections or heuristics. For example, Emsisoft Anti-Malware and Malwarebytes Anti-Malware both contain behavioral detection that can prevent many, if not most, ransomware infections from encrypting a computer.
Last, but not least, make sure you practice the following security habits, which in many cases are the most important steps of all:
For a complete guide on ransomware protection, you visit our How to Protect and Harden a Computer against Ransomware article.
Ransom Note Text:
How Zenis Ransomware encrypts a computer
 Start Checks
Start Checks
 Setup Ransom Note
Setup Ransom Note
cmd.exe /C vssadmin.exe delete shadows /all /Quiet
cmd.exe /C WMIC.exe shadowcopy delete
cmd.exe /C Bcdedit.exe /set {default} recoveryenabled no
cmd.exe /C Bcdedit.exe /set {default} bootstatuspolicy ignoreallfailures
cmd.exe /C wevtutil.exe cl Application
cmd.exe /C wevtutil.exe cl Security
cmd.exe /C wevtutil.exe cl System"
sql
taskmgr
regedit
backup
.txt, .doc, .docx, .xls, .xlsx, .ppt, .pptx, .odt, .jpeg, .png, .csv, .sql, .mdb, .sln, .php, .asp, .aspx, .html, .xml, .psd, .sql, .mp4, .7z, .rar, .m4a, .wma, .avi, .wmv, .csv, .d3dbsp, .zip, .sie, .sum, .ibank, .t13, .t12, .qdf, .gdb, .tax, .pkpass, .bc6, .bc7, .bkp, .qic, .bkf, .sidn, .sidd, .mddata, .itl, .itdb, .icxs, .hvpl, .hplg, .hkdb, .mdbackup, .syncdb, .gho, .cas, .svg, .map, .wmo, .itm, .sb, .fos, .mov, .vdf, .ztmp, .sis, .sid, .ncf, .menu, .layout, .dmp, .blob, .esm, .vcf, .vtf, .dazip, .fpk, .mlx, .kf, .iwd, .vpk, .tor, .psk, .rim, .w3x, .fsh, .ntl, .arch00, .lvl, .snx, .cfr, .ff, .vpp_pc, .lrf, .m2, .mcmeta, .vfs0, .mpqge, .kdb, .db0, .dba, .rofl, .hkx, .bar, .upk, .das, .iwi, .litemod, .asset, .forge, .ltx, .bsa, .apk, .re4, .sav, .lbf, .slm, .bik, .epk, .rgss3a, .pak, .big, wallet, .wotreplay, .xxx, .desc, .py, .m3u, .flv, .js, .css, .rb, .p7c, .pk7, .p7b, .p12, .pfx, .pem, .crt, .cer, .der, .x3f, .srw, .pef, .ptx, .r3d, .rw2, .rwl, .raw, .raf, .orf, .nrw, .mrwref, .mef, .erf, .kdc, .dcr, .cr2, .crw, .bay, .sr2, .srf, .arw, .3fr, .dng, .jpe, .jpg, .cdr, .indd, .ai, .eps, .pdf, .pdd, .dbf, .mdf, .wb2, .rtf, .wpd, .dxg, .xf, .dwg, .pst, .accdb, .mdb, .pptm, .pptx, .ppt, .xlk, .xlsb, .xlsm, .xlsx, .xls, .wps, .docm, .docx, .doc, .odb, .odc, .odm, .odp, .ods, .odt
 Zenis Encrypted Files
Zenis Encrypted Files
 Delete Backup Files
Delete Backup Files
.win, .wbb, .w01, .v2i, .trn, .tibkp, .sqb, .rbk, .qic, .old, .obk, .ful, .bup, .bkup, .bkp, .bkf, .bff, .bak, .bak2, .bak3, .edb, .stm
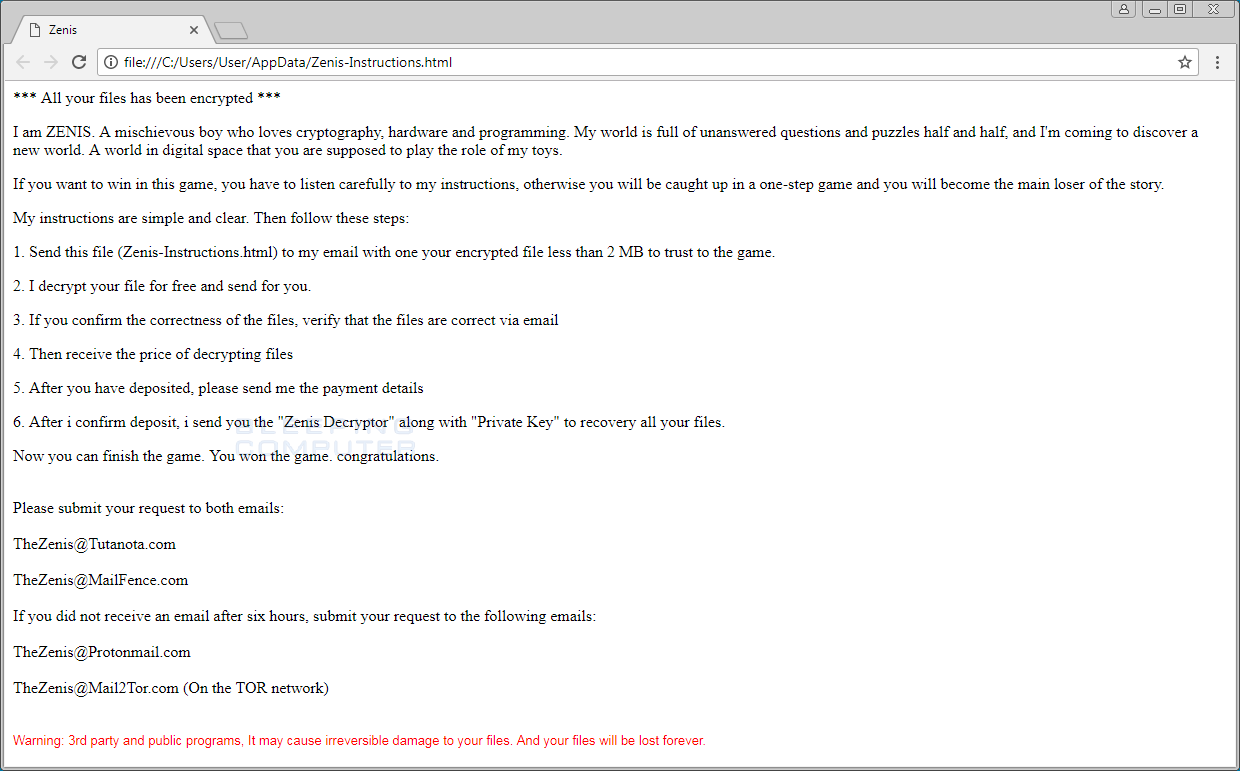 Zenis Ransom Note
Zenis Ransom Note
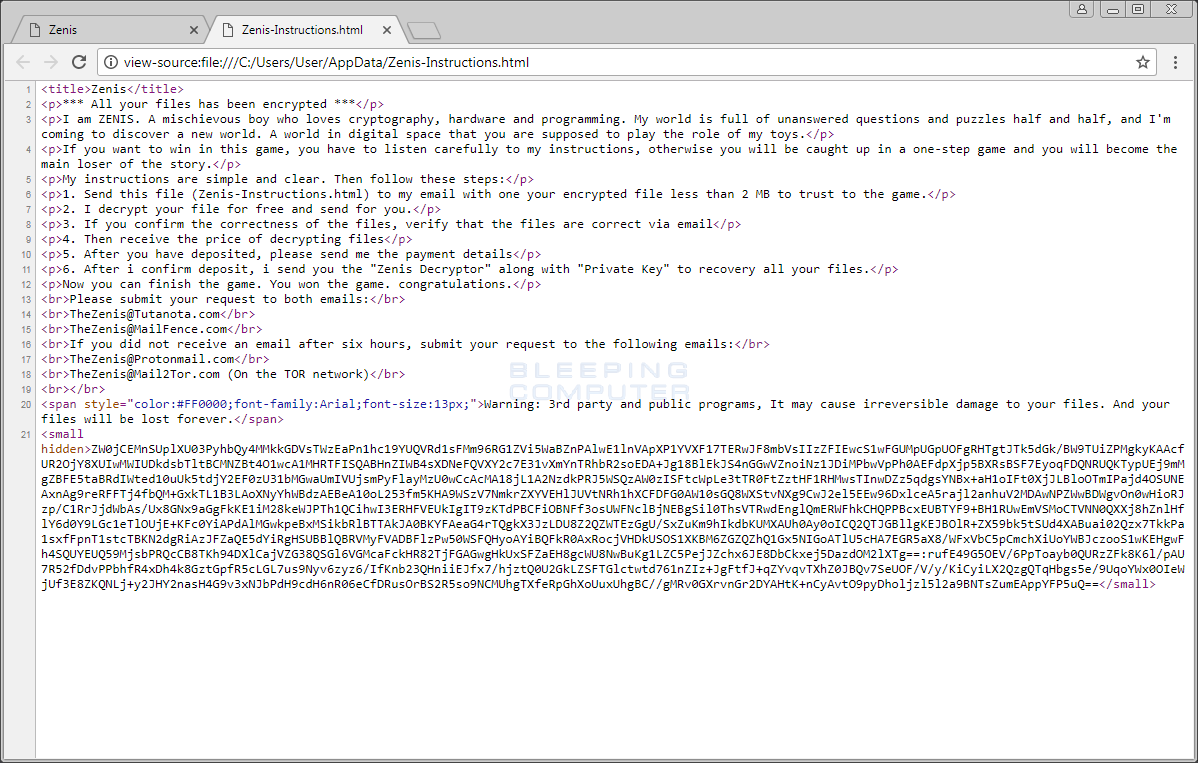 Ransom Note Source
Ransom Note Source
How to protect yourself from the Zenis Ransomware
IOCs
Hashes:
SHA256: 9730e03ca9d052875895b4ad7ba7914f69009fd5fb58d324ee35d3e45f90d768
Files:
Zenis-Instructions.html
Registry Keys:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\ZenisService "Active"
Associated Emails:
TheZenis@Tutanota.com
TheZenis@MailFence.com
TheZenis@Protonmail.com
TheZenis@Mail2Tor.com
*** All your files has been encrypted ***
I am ZENIS. A mischievous boy who loves cryptography, hardware and programming. My world is full of unanswered questions and puzzles half and half, and I'm coming to discover a new world. A world in digital space that you are supposed to play the role of my toys.
If you want to win in this game, you have to listen carefully to my instructions, otherwise you will be caught up in a one-step game and you will become the main loser of the story.
My instructions are simple and clear. Then follow these steps:
1. Send this file (Zenis-Instructions.html) to my email with one your encrypted file less than 2 MB to trust to the game.
2. I decrypt your file for free and send for you.
3. If you confirm the correctness of the files, verify that the files are correct via email
4. Then receive the price of decrypting files
5. After you have deposited, please send me the payment details
6. After i confirm deposit, i send you the "Zenis Decryptor" along with "Private Key" to recovery all your files.
Now you can finish the game. You won the game. congratulations.
Please submit your request to both emails:
TheZenis@Tutanota.com
TheZenis@MailFence.com
If you did not receive an email after six hours, submit your request to the following emails:
TheZenis@Protonmail.com
TheZenis@Mail2Tor.com (On the TOR network)
Warning: 3rd party and public programs, It may cause irreversible damage to your files. And your files will be lost forever.

